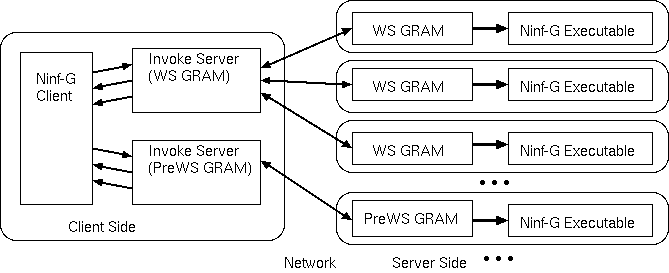
Figure 1: Interaction between the Ninf-G Client, Invoke Server and the Ninf-G Executable
This document describes how to develop a Ninf-G Invoke Server.
A Ninf-G Client invokes a Ninf-G Executable on the server machine when a function requiring initialization of function/object handles, such as grpc_function_handle_init(), is called. Ninf-G, Version 2, implements the remote process invocation using the Globus Toolkit's Pre-WS GRAM feature. Implemented using the Globus API, the invocation mechanism has been embedded in Ninf-G. In order to utilize other systems, such as WS GRAM, UNICORE, or Condor for remote process invocation, Ninf-G, Version 4, implements the invocation mechanism as a separate module called "Invoke Server." This design enables users and developers to implement and add a new Invoke Server that can utilize any job invocation mechanism.
Ninf-G Version 4.2.0 includes the following Invoke Servers:
Here is a typical flow of a Ninf-G Client application:
Initializes data structures used by the Ninf-G Client.
Creates a function/object handle which requests remote process invocation. The request will be processed and a Ninf-G Executable will be created on the server machine. When the Ninf-G Executable is created, it connects to the Ninf-G Client to establish a TCP connection between the Ninf-G Executable and the Ninf-G Client.
Calls the remote function, i.e. (3.1) the Ninf-G Client sends arguments to the Ninf-G Executable, (3.2) the Ninf-G Executable performs some form of computation, and (3.3) the Ninf-G Executable sends the results to the Ninf-G Client.
Requests the Ninf-G Executable to terminate its process. If an error occurs during the termination, the Ninf-G Client requests the Invoke Server to kill the Ninf-G Executable.
Frees the data structures used by the Ninf-G Client.
Invoke Server is required to implement initialization and finalization of the function/object handles which are described in steps (2) and (4).
The only requirement for underlying middleware is that the middleware must be capable of remote process invocation. Examples of such middleware include the Globus Toolkit Pre-WS GRAM, Globus Toolkit WS GRAM, Unicore, Condor, and SSH.
Invoke Server is an adapter for the underlying middleware and it
handles requests from a Ninf-G Client.
Invoke Server analyzes and processes the request sent from
the Ninf-G Client and replies to the Ninf-G Client.
For example, if Invoke Server receives a JOB_CREATE
request from the Ninf-G Client, Invoke Server creates a Job ID,
returns the Job ID to the Ninf-G Client,
and invokes the job processes called for in the request.
Invoke Server can be implemented using any language. The details of the protocol existing between the Ninf-G Client and Invoke Server are described in Section 2.
This section describes a sample RPC flow to a server called serverA
via the Invoke Server, IS_SAMPLE.
(1) A client configuration file that describes that
Invoke Server IS_SAMPLE is used for RPC to serverA
must be prepared.
(2) The Ninf-G Client requests Invoke Server
IS_SAMPLE to create a
function/object handle.
(3) The first time IS_SAMPLE is required to create
a function/object handle, the IS_SAMPLE process is spawned by
the Ninf-G Client on the same machine.
${NG_DIR}/bin/ng_invoke_server.IS_SAMPLE is a command
for spawning an IS_SAMPLE process.
(4) The Ninf-G Client and IS_SAMPLE
communicate using three pipes (stdin, stdout, and stderr).
(5) When grpc_function_handle_init() is called,
the Ninf-G Client sends JOB_CREATE request to
IS_SAMPLE,
followed by the required information
(e.g., the hostname and port number of the remote server),
and JOB_CREATE_END.
(6) When IS_SAMPLE receives
JOB_CREATE request,
IS_SAMPLE returns "S" to the Ninf-G Client,
which indicates that the request has been received by
the Invoke Server.
(7) IS_SAMPLE generates a new Job ID that corresponds
to the Request ID that was transferred with the JOB_CREATE
request, and notifies the Job ID to the Ninf-G Client.
Then, IS_SAMPLE invokes the remote processes
(Ninf-G Executable) on serverA using its underlying middleware.
(8) The Ninf-G Client waits for the reply from
IS_SAMPLE,
and notify of Job ID.
When the Ninf-G Client receives the reply and Job ID,
it resumes the execution without waiting for actual job invocation
on serverA.
(9) When the Ninf-G Executable is invoked on serverA,
it connects to the Ninf-G Client using Globus IO.
The connection is used for communication
(e.g., argument transfers from the Ninf-G Client to the Ninf-G Executable)
between the Ninf-G Client and the Ninf-G Executable.
IS_SAMPLE does nothing for grpc_call().
If the underlying middleware for IS_SAMPLE returns an error
on remote process invocation, IS_SAMPLE must notify
the Ninf-G Client that the job invocation has failed.
(10) When grpc_function_handle_destruct() is called, the Ninf-G Client requests the Ninf-G Executable to exit the process. This communication is carried out between the Ninf-G Client and the Ninf-G Executable. The Ninf-G Client does not wait for the Ninf-G Executables to be terminated.
(11) When the Ninf-G Executable exits the process,
the job status managed by IS_SAMPLE should be changed to
DONE,
and IS_SAMPLE notifies the Ninf-G Client of the change
in job status to DONE.
(12) The Ninf-G Client sends a JOB_DESTROY request to
IS_SAMPLE.
(13) IS_SAMPLE returns "S" to
the Ninf-G Client when it receives the JOB_DESTROY
request.
(14) IS_SAMPLE returns DONE to
the Ninf-G Client
if the state of the corresponding job is DONE.
Otherwise, IS_SAMPLE cancels the job and notifies
the Ninf-G Client of the change in status to DONE
when the cancellation is completed and the status of
the job actually becomes DONE.
(15) When grpc_finalize() is called,
the Ninf-G Client sends an EXIT request to
IS_SAMPLE.
(16) IS_SAMPLE returns "S" to
the Ninf-G Client when it receives the EXIT request.
The pipes between IS_SAMPLE and Ninf-G Client
(stdin, stdout, stderr) are closed after it.
(17) IS_SAMPLE cancels all jobs and wait
the termination of all jobs, and exit.
(18) When the Ninf-G Client receives an "S" from
IS_SAMPLE,
it continues its execution, and does not wait for the termination
of all jobs.
The following figure illustrates the interaction between the Ninf-G Client, Invoke Server, and the Ninf-G Executable.

Figure 1: Interaction between the Ninf-G Client, Invoke Server and the Ninf-G Executable
This section describes a detailed overview of Invoke Server and the protocol existing between a Ninf-G Client and Invoke Server.
Invoke Server is invoked when a Ninf-G Client initializes a function/object handle on the remote server which Ninf-G Client is configured to use with Invoke Server.
The maximum number of jobs per Invoke Server is limited. If the number of jobs exceeds the limit, a new Invoke Server is invoked.
Invoke Server exits the process if it receives an
EXIT request
from the Ninf-G Client.
This request is sent when the Ninf-G Client calls grpc_finalize().
Invoke Server also exits the process if it is managing the
maximum number of jobs and all jobs are terminated.
The Ninf-G Client and Invoke Server communicate using three pipes, created by the Ninf-G Client when the Invoke Server is invoked.
Ninf-G Client does not wait for the termination of Invoke Server
after the Ninf-G Client sends an EXIT request to
Invoke Server.
If the Ninf-G Client exits abnormally, the pipes will be disconnected. When Invoke Server detects that the pipes have been disconnected, Invoke Server must cancel all jobs and exit the process.
Invoke Server is implemented as a Unix executable or script file
which should be located in the ${NG_DIR}/bin directory.
It can be located in another directory if Invoke Server is
supplied with an absolute path to the executable file.
The file names used with Invoke Server must follow the naming convention of "ng_invoke_server" + suffix, where the suffix corresponds to rules for the underlying middleware used for remote process invocation.
Log file for Invoke Server can be specified as an optional argument of the Invoke Server command.
Example:
-l [Log file name]
If this option is specified, Invoke Server outputs logs to the file specified by this argument. Otherwise, logs are not recorded.
A Ninf-G Client and Invoke Server exchange three types of messages, Request, Reply, and Notify. A Request message is sent from a Ninf-G Client to Invoke Server. Reply and Notify messages are sent from Invoke Server to the Ninf-G Client. The Ninf-G Client assumes that a Reply message must be returned from Invoke Server when the Ninf-G Client sends a Request message. A Notify message is used to send messages from Invoke Server to the Ninf-G Client asynchronously. Three different pipes are used for sending these three types of message.
| Name | fd | direction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Request | stdin | Ninf-G | ----> | Invoke |
| Reply | stdout | Client | <---- | Server |
| Notify | stderr | <---- | ||
All messages are sent as plain text.
The Return code (<RET>) is
0x0d0a.
The Return code is a delimiter that determines the unit of
messages.
A Job ID is generated by Invoke Server.
Four Request messages,
JOB_CREATE, JOB_STATUS,
JOB_DESTROY, and EXIT
are supported.
JOB_CREATE
|
This request is used to create and invoke a new job.
Required information for job invocation is described as a
set of attributes that is transferred along with
a JOB_CREATE request.
The details of these attributes are described in
Section 2.2.2.4.
JOB_CREATE is the only request that is described
using multiple lines.
All the other requests can be described with a single line.
A Ninf-G Client transfers a Request ID to Invoke Server. Invoke Server generates a unique Job ID and returns it to the Ninf-G Client. The Job ID is used by the Ninf-G Client to specify the job.
When Invoke Server receives a JOB_CREATE request,
it must send a Reply message to the Ninf-G Client.
Then, Invoke Server generates a unique Job ID and notifies
the Ninf-G Client of the Job ID.
Finally, Invoke Server requests job invocation on remote servers
via the underlying middleware used with the Invoke Server.
JOB_STATUS
|
This request queries Invoke Server on the status of jobs.
The current version of Ninf-G4 and prior does not use this
JOB_STATUS request.
JOB_DESTROY
|
This request is used to terminate and destroy jobs.
Invoke Server cancels all jobs if it receives this request and
the corresponding jobs are not completed.
When Invoke Server confirms that all jobs are cancelled,
it sends DONE to the Ninf-G Client.
EXIT
|
This request is used to terminate Invoke Server.
If Invoke Server receives this EXIT request,
it must cancel all outstanding jobs and wait for their termination.
Invoke Server must send a Reply message to a Ninf-G Client if Invoke Server receives a Request message from that Ninf-G Client.
The reply to JOB_CREATE, JOB_DESTROY,
and EXIT messages is:
|
where S is sent in case of Success.
Otherwise, F is returned, followed by
<Error String>.
The reply to a JOB_STATUS message is:
|
Where <Status> is denoted as:
<Status> : [PENDING | ACTIVE | DONE | FAILED]
Each status indication indicates the status such that:
PENDING : the Ninf-G Executable is waiting for invocation.
ACTIVE : the Ninf-G Executable is already invoked.
DONE : the Ninf-G Executable is already done.
FAILED : the Ninf-G Executable exited abnormally.
A Notify message is used to send an asynchronous message from Invoke Server to a Ninf-G Client. Two types of Notify message are provided.
CREATE_NOTIFY
|
This is used to notify the Ninf-G Client of the Job ID. A Job ID is case sensitive and cannot include invisible characters.
STATS_NOTIFY
|
<Status> : [PENDING | ACTIVE | DONE | FAILED]
This message is used to send notification that the status of a job has been changed.
<String> can be any string,
and the <String> is stored in an output log.
It should be noted that the status of job can be changed from
PENDING to DONE.
JOB_CREATE RequestThis section describes the details of
a JOB_CREATE Request.
|
Attributes are placed between JOB_CREATE<RET>
and JOB_CREATE_DONE<RET>.
Only one attribute can occupy one line and one line must
include one and only one attribute.
Attributes can be placed in any order.
There are two types of attributes, mandatory attributes and
optional attributes. Invoke Server must return an error
if mandatory attributes are not included.
Any unknown optional attributes must be ignored.
The following is a list of attributes supported by Ninf-G.
Some of these attributes are provided for the Globus Toolkit's
Pre-WS GRAM and WS-GRAM.
Any new attribute can be defined using the
Client configuration file <SERVER> section
"invoke_server_option" attribute.
| name | mandatory | meanings |
|---|---|---|
| hostname | yes | Host name of the server |
| port | yes | Port number |
| jobmanager | no | Job Manager |
| subject | no | Subject of the GRAM |
| client_name | yes | Host name of the Ninf-G Client |
| executable_path | yes | Path of the Ninf-G Executable |
| backend | yes | Backend of the remote function (e.g., MPI) |
| count | yes | Number of Ninf-G Executables |
| staging | yes | A flag indicating if staging is used or not |
| argument | yes | Arguments for the Ninf-G Executable |
| work_directory | no | Working directory of the remote function |
| gass_url | no | The URL of GASS |
| redirect_enable | yes | A flag indicating redirection of stdout/stderr |
| stdout_file | no | file name of stdout |
| stderr_file | no | file name of stderr |
| environment | no | Environment variables |
| tmp_dir | no | temporary files directory |
| status_polling | yes | Interval of status polling |
| refresh_credential | yes | Interval of credential refresh |
| max_time | no | Maximum execution time |
| max_wall_time | no | Maximum wall clock time |
| max_cpu_time | no | Maximum CPU time |
| queue_name | no | Name of the queue |
| project | no | Name of the project |
| host_count | no | Number of executables per host |
| min_memory | no | Minimum size of requested memory |
| max_memory | no | Maximum size of requested memory |
| rsl_extensions | no | RSL extension |
Detailed description
Host name of the server machine.
The server port number on which the server is listening. The default value is depend on underlying middleware.
The job manager used on the server machine.
The certificate subject of the resource manager contact.
The host name of the client machine.
Absolute path of the Ninf-G Executable. The path represents a remote path if staging is off. Otherwise, the path represents a local path.
The method for launching the Ninf-G Executable is specified as
backend.
The value is NORMAL,
MPI, or BLACS.
If MPI or BLACS is specified,
the Ninf-G Executable must be invoked via the mpirun command.
The number of Ninf-G Executables to be invoked.
If the backend is MPI or BLACS,
count means the number of nodes.
The value is true if staging is on and Invoke Server must transfer the Ninf-G Executable file from the local machine to the remote machine.
An argument for the Ninf-G Executable is specified using this attribute. This attribute can specify one argument only, and multiple arguments must be specified one by one, by using this attribute for each one. The arguments must be passed to the Ninf-G Executable as arguments.
Example:
argument --client=...
argument --gass_server=...
This attribute specifies the directory in which the Ninf-G Executable is invoked.
This directory specifies the URL of the GASS server on the Client machine. This attribute is used for the Globus Toolkit's Pre-WS GRAM.
This attribute is set to true if the stdout/stderr of the Ninf-G Executable has been requested to be transferred to the Ninf-G Client.
If redirect_enable is set to true, this attribute specifies the name of the output file for stdout. Invoke Server must output the stdout to this file. The Ninf-G Client reads this file as an output file and writes the contents of the file to the stdout of the Ninf-G Client.
If redirect_enable is set to true, this attribute specifies the name of the output file of the stderr. Invoke Server must output the stderr to this file. The Ninf-G Client reads this file as an output file and writes the contents of the file to the stderr of the Ninf-G Client.
The environment variable for the Ninf-G Executable
is passed using this attribute.
The environment variable and its value are connected by =.
Only the variable is specified if it does not take a value.
Multiple environment variables must be specified one by one.
The directory in which temporal files are placed.
Invoke Server may need to check the status of jobs by polling the status of existing jobs. This attribute specifies the interval of the polling. The value is in seconds, and if it is not specified, the default value 0 is passed.
This attribute specifies the interval for refreshing credentials. The value is in seconds, and if it is not specified, the default value 0 is passed.
This attribute specifies the maximum time of the job.
This attributes specifies the maximum wall clock time of the job.
This attribute specifies the maximum cpu time of the job.
This attribute specifies the name of the queue to which the Ninf-G Executable should be submitted.
This attribute specifies the name of the project.
This attribute specifies the number of nodes.
This attribute specifies the minimum requirements for the memory size of the job.
This attribute specifies the maximum memory size of the job.
This attribute can be used to specify the RSL extension which is available for the Globus Toolkit's WS GRAM.
Invoke Server is specified by using the invoke_server attribute in the <SERVER> section.
invoke_server [type]
Type specifies the type of the Invoke Server, such as GT4py or UNICORE.
Invoke Server may require options for its execution. Such options can be specified by an option attribute in the <INVOKE_SERVER> section or by an invoke_server_option attribute in the <SERVER> section.
option [String]
invoke_server_option [String]
Multiple attributes can be specified in the <SERVER> or <INVOKE_SERVER> sections.
Invoke Server must check the status of jobs, and this may be implemented using polling. The polling interval can be specified by the status_polling attribute in the <INVOKE_SERVER> section.
status_polling [interval (seconds)]
The filename of the Invoke Server's execution log can be specified by the invoke_server_log attribute in the <CLIENT> section.
invoke_server_log [filename]
If this attribute is specified, Invoke Server outputs logs to a file with the specified filename and file type of that Invoke Server.
The log_filePath attribute in the <INVOKE_SERVER> section can be used to specify a log file for a specific Invoke Server.
log_filePath [Log file name]
The maximum number of jobs per Invoke Server can be limited by the max_jobs attribute in the <INVOKE_SERVER> section. If the number of requested jobs exceeds this value, the Ninf-G Client invokes a new Invoke Server and requests that Invoke Server to manage the new jobs.
max_jobs [maximum number of jobs]
If Invoke Server is not located in a pre-defined directory, the path attribute in <INVOKE_SERVER> can be used to specify the path of the Invoke Server.
path [path of the Invoke Server]
The Job Timeout function is managed by the Ninf-G Client. Invoke Server is not responsible for the timeout.
Redirect stdout/stderr is implemented using files.
JOB_CREATE request.